Welcome to the world of medieval fashion! In this article, we will delve into the captivating realm of medieval costumes, exploring their historical significance and timeless allure. Step back in time with us as we uncover the enchanting stories behind these exquisite garments that continue to captivate hearts and minds today.
The Most Common Types of Medieval Costumes Worn by Nobility
1. The Knight’s Armor
When you think of medieval costumes, the first thing that comes to mind is probably the knight’s armor. These suits of armor were not only functional in battle but also served as a symbol of status and power. Made from various materials such as steel and leather, they consisted of a helmet, breastplate, gauntlets, greaves, and other protective pieces. Each suit was customized to fit the individual knight and often featured intricate engravings or decorative elements.
2. The Queen’s Gown
No medieval costume collection would be complete without a stunning queen’s gown. These dresses were typically made from luxurious fabrics like velvet or silk and adorned with elaborate embroidery or gemstones. They featured long flowing sleeves and a fitted bodice that accentuated the wearer’s figure. To complete the look, queens often wore ornate headdresses or crowns.
3. The Lord’s Tunic
For the male nobility, the lord’s tunic was a staple piece in their medieval wardrobe. These tunics were made from high-quality fabrics like wool or linen and featured rich colors such as deep reds or vibrant blues. They were often decorated with intricate patterns or coats of arms to showcase the wearer’s heritage and social standing.
4. The Lady’s Gown
The lady’s gown was another popular choice for noblewomen during the medieval period. These dresses were characterized by their full skirts, fitted bodices, and delicate details such as lace trim or embroidery. They were typically made from lightweight fabrics like silk or satin and came in an array of colors to suit each lady’s personal style.
List of common elements in medieval noble costumes:
- Intricate engravings or decorative elements on knight’s armor
- Luxurious fabrics like velvet or silk for queen’s gowns
- Elaborate embroidery or gemstones on queen’s gowns
- Ornate headdresses or crowns for queens
- High-quality fabrics like wool or linen for lord’s tunics
- Intricate patterns or coats of arms on lord’s tunics
- Full skirts, fitted bodices, and delicate details for lady’s gowns
- Lace trim or embroidery on lady’s gowns
- Variety of colors available for lady’s gowns
As a cosplay store, we understand the allure of dressing up as a noble from the medieval era. Whether you choose to don the impressive knight’s armor, embody the elegance of a queen’s gown, exude power in a lord’s tunic, or embrace femininity with a lady’s gown, these costumes allow you to transport yourself back in time and experience the grandeur of the nobility.
2. The Differences in Clothing Between Medieval Peasants and the Upper Class
Peasant Clothing
Medieval peasants, who made up the majority of the population, had limited resources and typically wore simple and practical clothing. Their garments were often made from rough and coarse fabrics such as wool or linen. Peasant men commonly wore tunics that reached their knees, along with trousers or breeches. Women would wear long dresses known as gowns, which were often cinched at the waist with a belt. Both men and women would also wear cloaks or hoods to protect themselves from the elements.
Upper Class Clothing
The upper class during medieval times had access to more luxurious materials and could afford elaborate clothing. Noble men would wear fitted tunics made from fine fabrics like silk or velvet, often adorned with intricate embroidery or jewels. They also favored long robes and capes for formal occasions. Noblewomen would wear elegant gowns made from expensive fabrics, with elaborate sleeves and bodices that accentuated their figures. They would accessorize with jewelry such as necklaces, rings, and brooches.
Differences in Style
- Peasant clothing was plain and functional, while upper-class clothing was ornate and fashionable.
- Peasants primarily wore earthy tones such as browns and greens, while the upper class favored vibrant colors like reds, purples, and gold.
- The upper class had access to more varied styles of clothing due to their wealth, whereas peasants had simpler garments that were easier to produce.
Social Significance
The stark contrast in clothing between peasants and the upper class served as a visual representation of social hierarchy during the medieval period. The sumptuous attire of the nobility displayed their wealth and status, while the modest clothing of peasants reflected their lower social standing. These distinct styles of dress reinforced the divide between the classes and reinforced the idea that one’s clothing was a reflection of their place in society.
Impact on Daily Life
The differences in clothing between peasants and the upper class also had practical implications. Peasant clothing was designed for durability and functionality, allowing them to perform labor-intensive tasks without hindrance. The upper class, on the other hand, had more restrictive and elaborate garments that were not suitable for physical work. Their clothing often required assistance to put on or remove, reflecting their reliance on servants for daily tasks.
3. Common Materials Used to Make Medieval Costumes
Natural Fibers
One of the most common materials used to make medieval costumes was natural fibers such as wool, linen, and silk. Wool was a popular choice due to its availability and ability to provide warmth during the colder months. Linen, made from flax plants, was lightweight and breathable, making it suitable for summer garments. Silk, although more expensive and luxurious, was favored by the nobility for its softness and sheen.
Fur and Leather
In addition to natural fibers, fur and leather were often used in the construction of medieval costumes. Fur provided both warmth and a touch of luxury, with ermine being particularly prized for its white color and black-tipped tails. Leather was commonly used for outerwear such as coats and boots due to its durability and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions.
4. Rules and Regulations Regarding the Colors of Medieval Costumes
In medieval times, there were strict rules and regulations regarding the colors that could be worn in costumes. The choice of colors often reflected social status, with certain colors reserved for nobility or royalty. For example:
Purple:
- Purple was considered a royal color in many parts of Europe during the medieval period.
- It symbolized wealth, power, and authority.
- Only members of the royal family or high-ranking nobles were allowed to wear purple garments.
Red:
- Red was associated with passion, love, and courage.
- It could be worn by both men and women but was particularly popular among knights.
- The intensity of red varied, with brighter shades reserved for higher-ranking individuals.
5. Changing Fashion Trends Throughout the Medieval Period
The fashion trends in medieval costumes evolved throughout the different periods within the Middle Ages. Here are some key changes:
Early Medieval Period (5th-10th century):
- During this period, clothing was mainly functional and practical.
- Tunics and long robes were common garments for both men and women.
- Colors were often muted, with earth tones like brown, beige, and gray prevailing.
High Medieval Period (11th-13th century):
- Fashion became more elaborate and decorative during this period.
- Women’s dresses featured fitted bodices and flowing skirts.
- Men’s garments included tight-fitting tunics and hose.
Late Medieval Period (14th-15th century):
- Fashion became more extravagant with the introduction of elaborate headwear like hennins for women.
- Men’s clothing saw the rise of doublets and codpieces as fashion statements.
- Brighter colors such as deep blues, purples, and greens were popular among the wealthy.
Please note that these are just general trends, and specific variations existed across regions.
6. The Role of Accessories in Completing a Medieval Costume
Accessories played a crucial role in completing a medieval costume, adding both functionality and style. Some common accessories used during this period include:
Hats and Headgear:
In medieval times, hats served both practical purposes such as protection from weather elements as well as indicating social status. Some popular headwear choices included:
Caps:
- Simple caps made from wool or linen were worn by both men and women.
- They provided basic head covering and warmth.
Hennins:
- Hennins were tall, cone-shaped hats worn by noblewomen during the late medieval period.
- They were often decorated with veils and jewels, symbolizing wealth and high social standing.
Jewelry:
Jewelry was an important accessory for both men and women in medieval costumes. It served as a status symbol and added visual appeal to the overall outfit. Common types of jewelry included:
Necklaces:
- Necklaces made from precious metals such as gold or silver were worn by the wealthy.
- Gemstones like rubies, sapphires, and pearls were often incorporated into necklace designs.
Rings:
- Rings adorned with gemstones or engraved with family crests were popular among nobles.
- They were often worn on multiple fingers as a display of wealth and power.
These accessories helped individuals express their personal style while adhering to the fashion norms of the medieval era.
Please let me know if you would like me to continue expanding on any other subheadings.
7. Hairstyles and Headwear Associated with Medieval Costumes
Hairstyles
During the medieval era, hairstyles played a significant role in completing the overall look of a costume. Women often wore their hair long and flowing, with braids or twists incorporated for added decoration. These hairstyles were often adorned with ribbons, flowers, or jeweled accessories to add a touch of elegance. Men, on the other hand, commonly sported shorter haircuts that were neatly groomed and sometimes styled into simple curls or waves.
Headwear
Headwear was an essential component of medieval costumes as it helped to signify social status and occupation. Women typically wore veils or wimples, which covered their hair and necks, while men often donned hats or hoods made from various materials such as wool or felt. Additionally, crowns and tiaras were reserved for royalty and nobility to symbolize their elevated position in society.
Overall, hairstyles and headwear played a crucial role in enhancing the authenticity and visual appeal of medieval costumes by complementing the clothing styles of the time.
8. Gender Differences in Clothing Styles During the Medieval Era
Women’s Clothing
In medieval times, women’s clothing varied depending on their social status. Noblewomen wore elaborate gowns made from luxurious fabrics such as silk or velvet. These dresses featured fitted bodices, long flowing sleeves, and voluminous skirts that were often adorned with intricate embroidery or beading. Peasant women, on the other hand, wore simpler garments made from linen or woolen fabric. Their dresses consisted of loose-fitting tunics that reached their ankles.
Men’s Clothing
Men’s clothing during the medieval era also differed based on social class. Noblemen typically wore tunics made from fine fabrics, such as silk or brocade, which were tailored to fit their bodies. These tunics were often embellished with decorative trimmings and featured long sleeves. Peasant men, on the other hand, wore more practical attire consisting of simple tunics and trousers made from sturdy materials like wool or linen.
Similarities
Despite these differences, there were some similarities in clothing styles between genders. Both men and women wore various layers of clothing for warmth and modesty. Additionally, both genders often wore outer garments such as cloaks or mantles to protect themselves from the elements.
Overall, gender differences in medieval clothing styles were primarily influenced by social status and occupation, with nobility showcasing more elaborate and luxurious garments compared to the simpler attire worn by peasants.
9. Influence of Religious Beliefs on Design and Style of Medieval Costumes
Catholic Church Influence
Religious beliefs held a significant influence on the design and style of medieval costumes, particularly through the dominance of the Catholic Church during this period. The Catholic Church played a central role in society, dictating not only religious practices but also fashion trends. The church’s teachings regarding modesty heavily influenced the cut and coverage of garments worn by both men and women.
Symbols and Embellishments
Religious symbols were often incorporated into medieval costumes as a way to display one’s faith. Crosses, crucifixes, or images of saints could be found embroidered onto garments or worn as pendants or brooches. Additionally, religious festivals and ceremonies required specific attire that adhered to church guidelines.
Influence on Clergy Clothing
The influence of religious beliefs was most evident in the clothing worn by members of the clergy. Priests, monks, and nuns followed strict dress codes that reflected their devotion to God. These garments often featured simple designs and muted colors, emphasizing humility and detachment from worldly possessions.
In conclusion, religious beliefs had a profound impact on the design and style of medieval costumes. The Catholic Church’s teachings regarding modesty and symbolism influenced the cut, embellishments, and overall appearance of garments worn during this era.
10. Regional Variations in Medieval Costume Styles Across Europe
England
Medieval costume styles varied across different regions of Europe, with England showcasing its unique fashion trends. In England, women’s clothing consisted of fitted gowns with tight bodices and full skirts. These gowns were often made from luxurious fabrics such as silk or velvet and featured elaborate embroidery or beading. Men in England wore tunics that reached their knees and were typically made from wool or linen.
Italy
In Italy, fashion was heavily influenced by the Renaissance movement during the later medieval period. Women’s dresses in Italy featured more pronounced waistlines and intricate patterns inspired by classical art. Men’s attire included doublets, which were close-fitting jackets worn over shirts, along with breeches that reached the knee.
France
French medieval costume styles emphasized elegance and sophistication. Women in France wore long flowing gowns with fitted bodices that accentuated their curves. These gowns were often made from richly colored fabrics adorned with ornate embroidery or lace. Men’s clothing in France included tunics with wide sleeves and hose that covered their legs.
Overall, regional variations in medieval costume styles across Europe showcased the diverse cultural influences during this era. Each region had its own unique fashion trends that reflected its history, social norms, and artistic developments.
11. Key Elements Distinguishing a Knight’s Armor from a Regular Medieval Costume
Metal Construction
One of the key elements distinguishing a knight’s armor from a regular medieval costume is the use of metal construction. While regular medieval costumes were typically made from fabric, a knight’s armor consisted of various metal components such as plates, chainmail, and helmets. This metal construction provided superior protection during battles and emphasized the knight’s status as a warrior.
Layered Protection
Another distinguishing feature of knight’s armor was its layered protection. A typical knight’s armor included multiple layers of metal plates that covered different parts of the body, such as the chest, arms, legs, and head. These layers were designed to provide maximum protection while allowing for flexibility and movement in combat.
Specialized Components
Knight’s armor also featured specialized components that were not found in regular medieval costumes. These included gauntlets to protect the hands, greaves to shield the shins, and a visor or faceplate to protect the face during battle. These additional components further enhanced the defensive capabilities of a knight’s armor.
In conclusion, key elements that distinguished a knight’s armor from a regular medieval costume included its metal construction, layered protection, and specialized components designed for combat purposes.
12. Impact of Social Status on Quality and Intricacy of Medieval Costumes
Nobility
Social status had a significant impact on the quality and intricacy of medieval costumes. Nobility enjoyed access to luxurious fabrics such as silk or velvet, which were often imported from distant lands. Their garments featured intricate embroidery or beading done by skilled artisans. The higher their social standing, the more elaborate their costumes became.
Peasantry
Peasants had limited resources and relied on locally available materials for their clothing. Their garments were simpler in design and made from practical fabrics like wool or linen. Peasant costumes focused more on functionality rather than intricate details, as their primary concern was to stay warm and protected.
Middle Class
The middle class occupied a position between nobility and peasantry, and their costumes reflected this status. Their garments were often made from more affordable fabrics such as cotton or wool, but they still incorporated some decorative elements like trimmings or embroidery. The quality and intricacy of middle-class costumes varied depending on the individual’s wealth and social standing within this group.
In summary, social status played a crucial role in determining the quality and intricacy of medieval costumes. Nobility showcased luxurious fabrics and intricate designs, while peasants focused on practicality. The middle class found a balance between affordability and decoration based on their individual means.
13. Rules and Guidelines for Appropriate Attire During Different Occasions in the Middle Ages
Courtly Events
During courtly events in the Middle Ages, strict rules governed appropriate attire based on one’s social status. Nobility were expected to wear lavish garments made from expensive fabrics with intricate detailing. Men typically wore tunics or doublets adorned with elaborate embroidery, while women donned gowns with voluminous skirts and ornate accessories.
Religious Ceremonies
Religious ceremonies required modest attire that adhered to church guidelines. Both men and women were expected to cover their shoulders, arms, and legs. Women often wore veils or wimples to cover their hair, while men wore simple tunics or robes made from plain fabrics.
Everyday Life
In everyday life during the Middle Ages, clothing choices were influenced by practicality rather than strict rules. Peasants wore simple tunics or dresses made from sturdy materials like wool or linen for durability. The working class often wore garments that allowed ease of movement for their specific occupations.
Overall, rules and guidelines for appropriate attire during different occasions in the Middle Ages were influenced by social status, religious beliefs, and practicality. These guidelines ensured that individuals dressed appropriately for their roles and respected societal norms.
14. Advancements in Textile Production and Availability of Materials for Making Medieval Costumes
Introduction of the Spinning Wheel
One significant advancement in textile production during the medieval era was the introduction of the spinning wheel. Prior to this invention, fibers were spun by hand using a drop spindle, which was a slow and labor-intensive process. The spinning wheel revolutionized textile production by allowing fibers to be spun more efficiently, resulting in an increased availability of yarn for making garments.
Importation of Luxurious Fabrics
During the medieval period, trade routes expanded, leading to an increase in the importation of luxurious fabrics from distant lands. Silk, velvet, brocade, and damask became popular choices for noble garments due to their exquisite textures and vibrant colors. The availability of these imported fabrics allowed for greater variety and sophistication in medieval costumes.
Rise of Guilds
The rise of guilds also contributed to advancements in textile production during the Middle Ages. Guilds were associations formed by skilled craftsmen who specialized in various trades, including weaving and dyeing. These guilds established standards for quality control and techniques, resulting in improved craftsmanship and a wider range of available materials for making costumes.
In conclusion, advancements in textile production during the medieval era, such as the introduction of the spinning wheel and increased importation of luxurious fabrics, greatly influenced the availability and quality of materials used for making medieval costumes. Additionally, guilds played a crucial role in ensuring high standards and innovation within the textile industry.
In conclusion, medieval costumes are a fantastic way to transport yourself to a bygone era and add a touch of history to your wardrobe. Whether you’re attending a themed party or simply want to embrace your inner knight or princess, our cosplay products can help you bring your medieval fantasies to life. So why wait? Check out our range of costumes and accessories today and get in touch with us to make your medieval dreams come true!

How did people dress in the Middle Ages?
Men in the peasant class would wear either stockings or tunics, while women would wear long gowns paired with sleeveless tunics and wimples to cover their hair. During the winter, they would wear sheepskin cloaks, woolen hats, and mittens to protect themselves from the cold and rain. To keep their feet dry, they would wear leather boots with wooden patens over them.
What do you wear under a medieval dress?
In the Middle Ages, women wore a chemise underneath all of their clothing. The purpose of the chemise was to keep the outer clothing clean by absorbing sweat and oils from their bodies. It was also commonly used as a nightgown. Women would wear multiple layers of skirts over the chemise, along with pantaloons or bloomers.
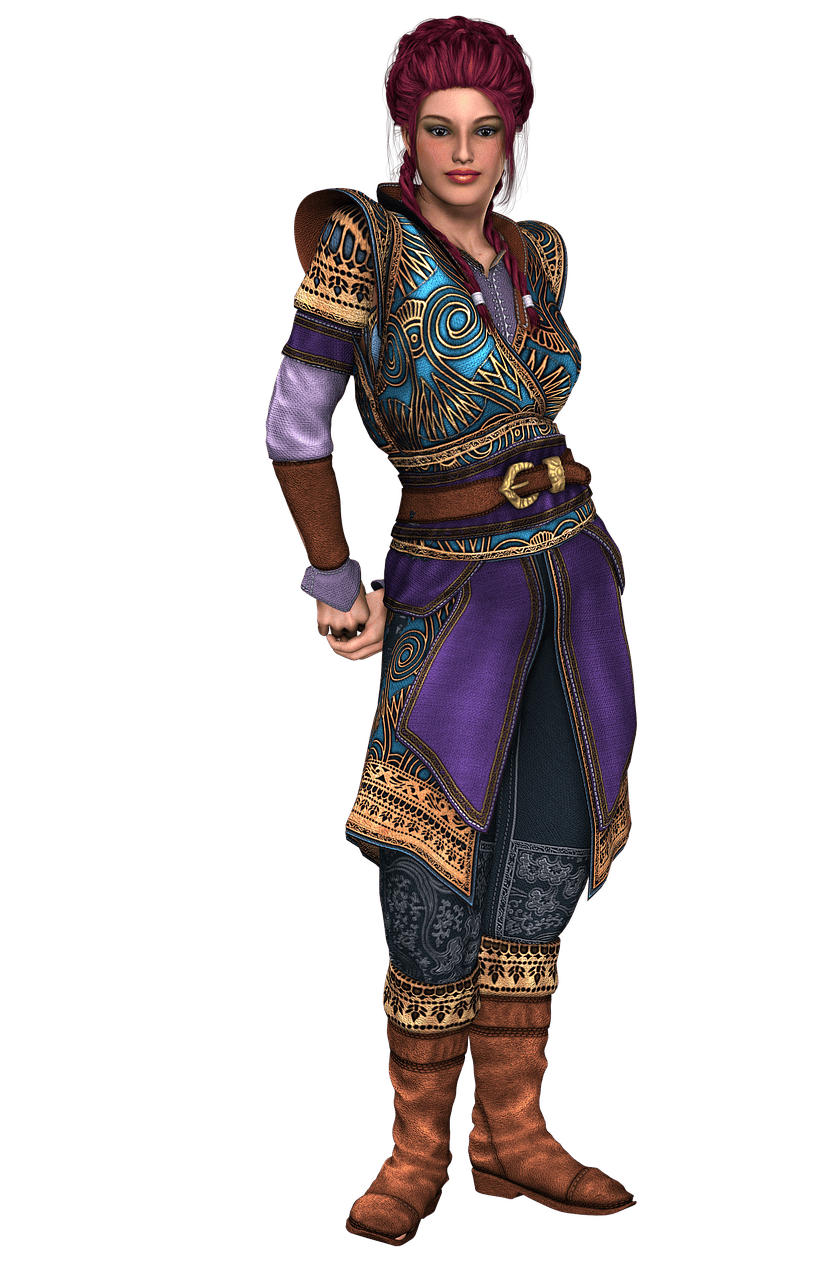

What is Renaissance costume?
In the Renaissance period, women’s fashion revolved around long and flowing dresses with high-waisted designs and puffy sleeves. The style of sleeves also changed during this time, with the funnel or trumpet-style sleeve, which was narrow at the top and wide at the bottom, gaining popularity in certain regions.
What is a medieval outfit called?
Common clothing items during this time included the smock, hose, kirtle, gown, belt, surcoat, girdle, cape, hood, and bonnet. Wealthy women preferred luxurious fabrics like silk and fine linen, while those in lower social classes wore wool and rougher linen.
How to make a Tudor costume?
To achieve the appearance of a traditional Tudor boy, begin by wearing long football socks pulled up over three-quarter or full length pants. Pair this with a collarless ‘Grandad’ style shirt and a waistcoat for the upper body. Complete the look with a dark colored hat that has a wide, floppy brim.
What did ladies wear in medieval times?
Women’s attire included a basic undergarment known as a chemise, which was typically crafted from linen. On top of the chemise, women would don one or multiple floor-length tunics, also referred to as gowns or kirtles.